Nós usamos o Presente Contínuo (Present Progressive or Present Continuous):
🔸 para descrever ações que ocorrem no momento em que se fala
She is eating pizza at the moment 🍕
(Ela está comendo pizza no momento)
🔸 para ações longas que estão em progresso no momento em que se fala
He is learning how to surf 🏄♂️
(Ele começou a aprender a surfar – e ainda não terminou)
🔸 para ações temporárias
I‘m working in France this month. 🇫🇷
(Eu estou trabalhando na França este mês)
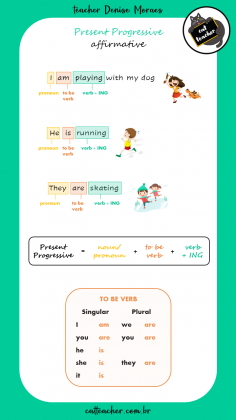
A estrutura do Presente Contínuo é formada pelo verbo TO BE + um verbo principal no gerúndio (ou seja, com ING no final). Aqui as sentenças estão na AFIRMATIVA:
John is riding a bike 🚵♂️
(John está andando de bicicleta)
I am taking a bath 🛀
(Eu estou tomando banho)
They are fighting 🤼♂️
(Eles estão lutando)
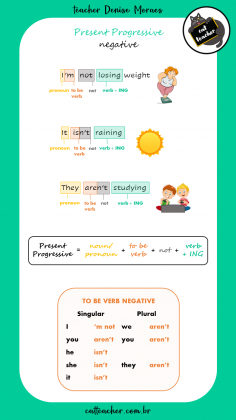
Já na NEGATIVA coloca-se o NOT logo após o verbo TO BE:
John is not riding a bike 🚵♂️
John isn’t riding a bike 🚵♂️ (short form)
(John não está andando de bicicleta)
I am not taking a bath 🛀
I‘m not taking a bath 🛀 (short form)
(Eu não estou tomando banho)
They are not fighting 🤼♂️
They aren’t fighting 🤼♂️ (short form)
(Eles não estão lutando)
Na estrutura INTERROGATIVA o verbo TO BE é posicionado ANTES do nome/pronome:
Is John riding a bike? 🚵♂️
(John está andando de bicicleta?)
Am I taking a bath? 🛀
(Eu estou tomando banho?)
Are they fighting? 🤼♂️
(Eles estão lutando?)