Nós usamos o Present Progressive for Future Arrangements (Presente Contínuo para se referir ao futuro) para falar de fatos que ocorrerão no futuro.
I‘m meeting my friends for pizza tonight 🍕
(Eu vou encontrar meus amigos para comer pizza hoje à noite)
COMO DIFERENCIAR?
Quando o Presente Contínuo se refere ao agora, ele geralmente vem acompanhado de expressões sobre o momento presente, como now, right now, at the moment, this month, etc.
Quando o Presente Contínuo se refere ao futuro, ele vem acompanhado da data futura em que o evento ocorrerá, como tonight, tomorrow, next Monday, in two weeks, later, etc.
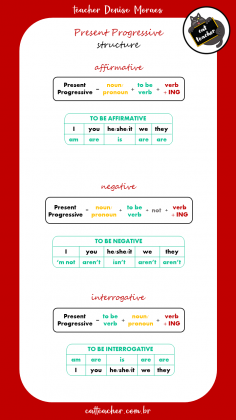
A estrutura do Presente Contínuo para se referir ao futuro é formada pelo verbo TO BE + um verbo principal no gerúndio (ou seja, com ING no final). Aqui as sentenças estão na AFIRMATIVA:
John is riding a bike next week 🚵♂️
(John andará de bicicleta semana que vem)
I am taking a bath later 🛀
(Eu tomarei banho mais tarde)
They are fighting this evening 🤼♂️
(Eles lutarão nesta noite)
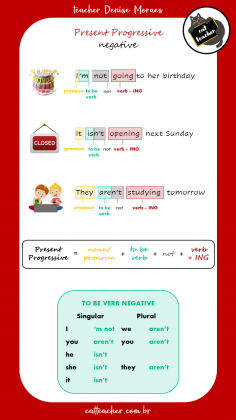
Já na NEGATIVA coloca-se o NOT logo após o verbo TO BE:
John is not riding a bike next week 🚵♂️
John isn’t riding a bike next week 🚵♂️ (short form)
(John não andará de bicicleta semana que vem)
I am not taking a bath later 🛀
I‘m not taking a bath later 🛀 (short form)
(Eu não tomarei banho mais tarde)
They are not fighting this evening 🤼♂️
They aren’t fighting this evening 🤼♂️ (short form)
(Eles não lutarão nesta noite)
Na estrutura INTERROGATIVA o verbo TO BE é posicionado ANTES do nome/pronome:
Is John riding a bike next week? 🚵♂️
(John andará de bicicleta semana que vem?)
Am I taking a bath later? 🛀
(Eu tomarei banho mais tarde?)
Are they fighting this evening? 🤼♂️
(Eles lutarão nesta noite?)